Fecha: 4 de Julio de 2024.
Hora: 11:00h.
Lugar: Salón de Grados Facultad de Ciencias.
Contacto del seminario: Miguel A. Galindo Cuesta
El seminario constará de las siguientes dos charlas (30min + preguntas) impartidas por los dos conferenciantes.
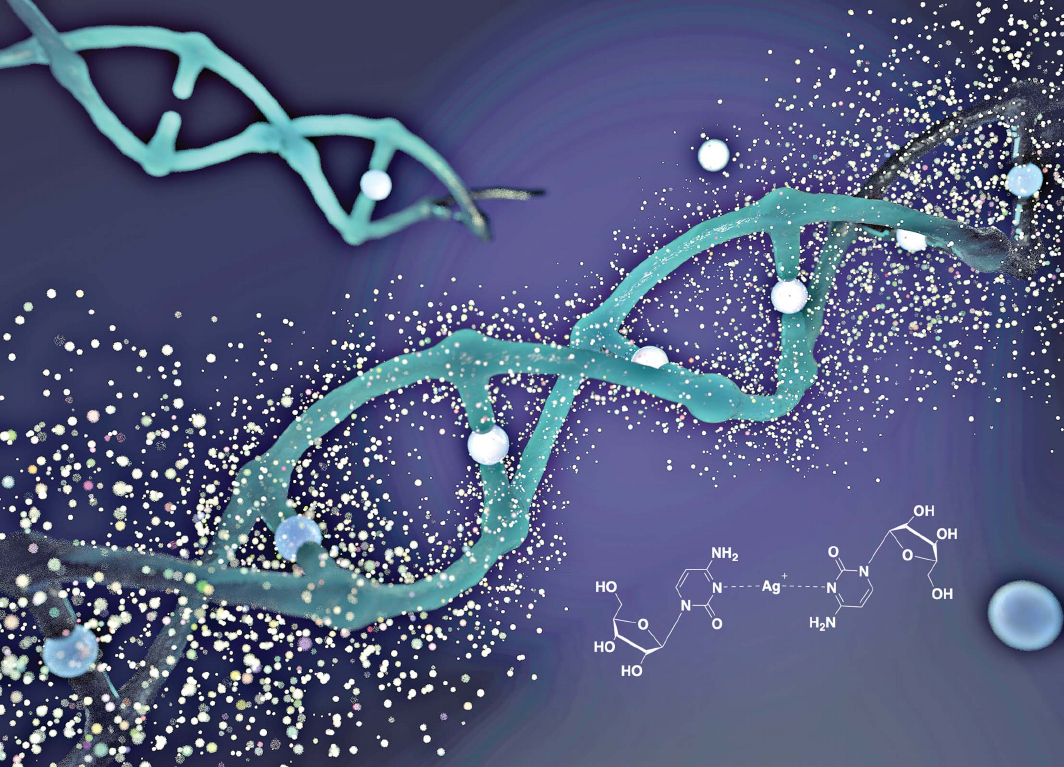
A coordination chemistry approach to the functionalisation of DNA... towards opto-electronics with metallo-DNA
Ponente: Prof. Andrew Houlton. School of Natural and Environmental Sciences, Newcastle University (Reino Unido).
Resumen: DNA is now an established component in the design of molecular-based nanostructured architectures due to its predictable self-assembly and reliable synthesis. Metal-ion binding has been explored in an effort to introduce new features/properties into DNA structures and elegant highly organised metallo-arrays have been demonstrated. Here, a distinct approach to this is described using thio-modified nucleosides. This allows the assembly of coordination polymer chains that exhibit a range of useful opto-electronic properties such as electrical conduction and circularly polarised luminescence (CPL).
Designer DNA-based nanostructures for therapeutic delivery
Ponente: Dra. Siliva Hernández Ainsa. Instituto de Nanociencia y Materiales de Aragón (INMA), CSIC-Universidad de Zaragoza.
Resumen: DNA nanotechnology is a unique synthetic tool for the reproducible preparation of biodegradable and tailored nanomaterials. The fabrication process is programmable and robust as it relies on the accurate specificity of the Watson-Crick-Franklin base-pairing interactions. Remarkably, the dimensions and functionalities of these DNA-based constructs can be customized and precisely controlled at the nanoscale level, which is key for some biomedical applications.
In this seminar, I will show how we can exploit these unique characteristics to obtain tailored DNA-based nanostructures (DNS) for the delivery of therapeutic agents targeting cancer and cardiac diseases.
Regarding cancer, we have prepared a set of simple DNS with subtle structural modifications and investigated their overall capabilities as nanocarriers for chemotherapy by evaluating their biological stability, their cellular internalisation, their ability to trap the anticancer drug doxorubicin as well as their effect on the viability of cancer cells.
In relation to cardiac disease, we have developed DNS for gene therapy finely folded with precise sequences for the trapping of a specific microRNA (miR) whose overexpression is associated to cardiac aging. We have studied the efficacy and specificity of miR capture by DNS in vitro and in cardiomyocytes of human origin obtained through iPSC differentiation.
I will finally show the possibility to create hybrid carriers by adapting DNS to interact with synthetic liposomes as stimuli-responsive containers or with synthetic polymers through innovative bio-conjugation strategies with the aim of maximising the biological performance of our nanomaterials.